

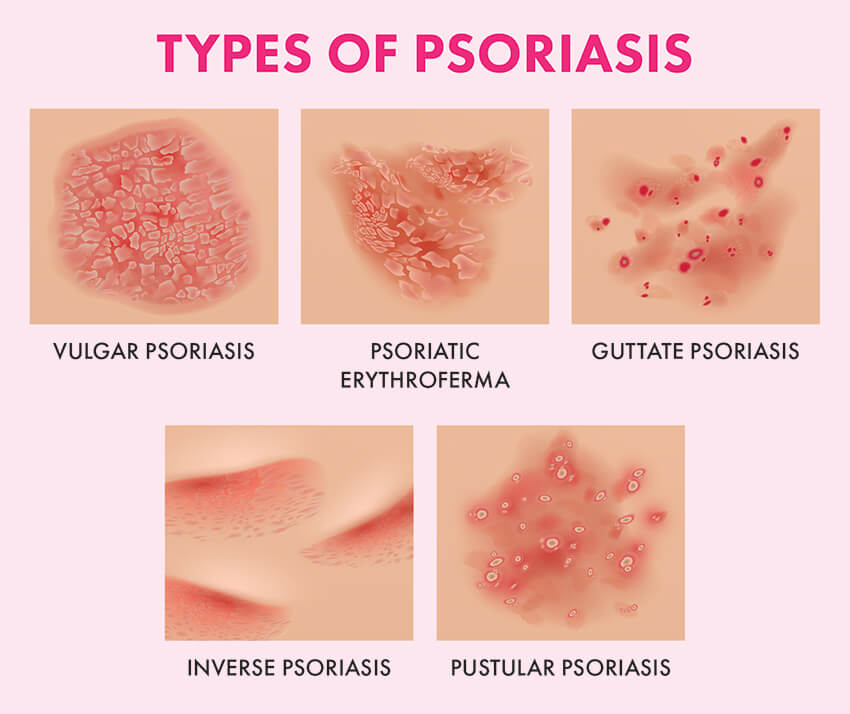
Psoriasis is a condition of the skin characterized by itchy rashes which appear and disappear on its own, anywhere on the body.
There is no exact cause of psoriasis but it’s known to be an autoimmune condition.There is inflammation in the skin which causes increased production of the skin cells.Normally, new skin cells are produced and replaced at a constant rate, in about 10-30 days. Psoriasis causes increased skin production leading to accelerated turnover of cells every 3-4 days.
Psoriasis often develops between the ages of 15 to 35, but it can occur at any age. About 10 to 15 percent of those with psoriasis get it before age 10. Some infants have psoriasis, although this is a rare scenario . Men and women develop psoriasis at equal rates.
At least 10 percent of the general population inherits one or more of the genes that create a predisposition to psoriasis. However, only two percent to three percent of the population develops the disease. So having psoriasis in your family has higher risk, but getting psoriasis is not a certainty.
Psoriasis triggers are not universal , however established psoriasis triggers include:
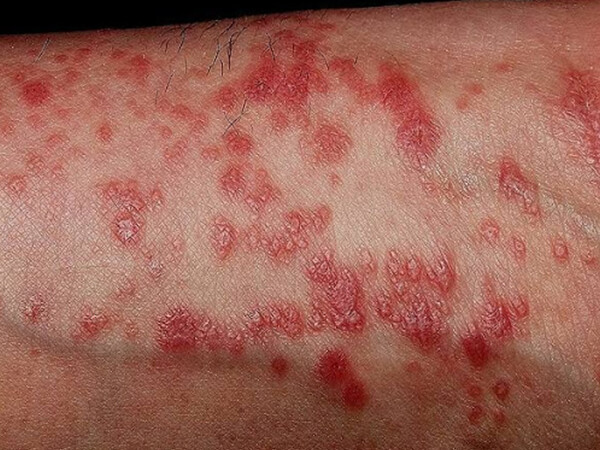
Lichen planus is a skin rash triggered by the immune system. It’s not known why the immune response occurs. There may be several contributing factors, and each case is different. Potential causes include:

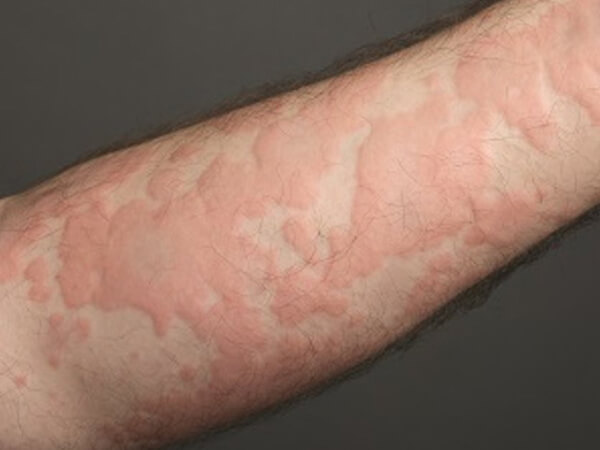
Urticaria, also known as hives, is an outbreak of swollen, pale red bumps or plaques (wheals) on the skin that appear suddenly -- either as a result of the body's reaction to certain allergens, or for unknown reasons. Hives usually cause itching, but may also burn or sting.
Contact Us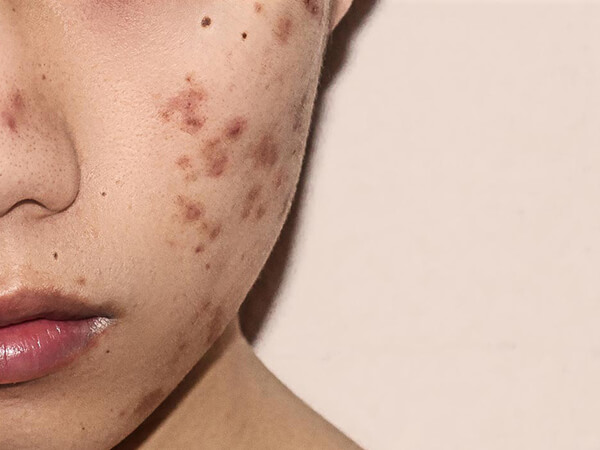
Acne scarring can sometimes develop as a complication of acne. Any type of acne spot can lead to scarring, but it's more common when the most serious types of spots (nodules and cysts) burst and damage nearby skin. Scarring can also occur if you pick or squeeze your spots, so it's important not to do this.
Contact Us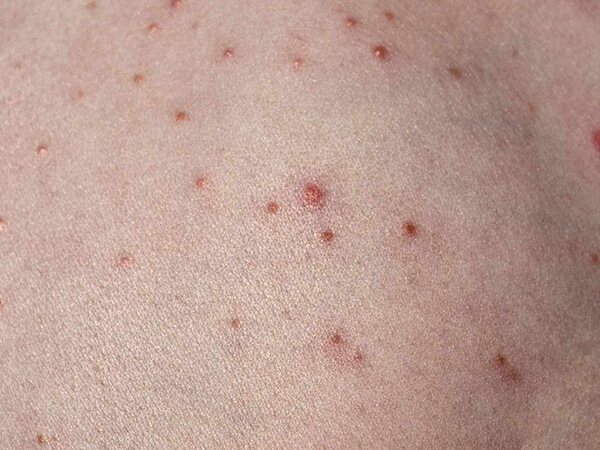
Common skin infections include cellulitis, erysipelas, impetigo, folliculitis, and furuncles and carbuncles. Cellulitis is an infection of the dermis and subcutaneous tissue that has poorly demarcated borders and is usually caused by Streptococcus or Staphylococcus species.
Contact Us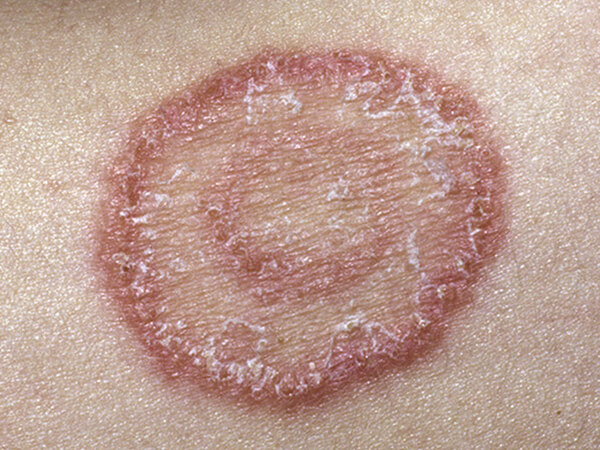
A fungal infection, also called mycosis, is a skin disease caused by a fungus. There are millions of species of fungi. They live in the dirt, on plants, on household surfaces, and on your skin. Sometimes, they can lead to skin problems like rashes or bumps.
Contact Us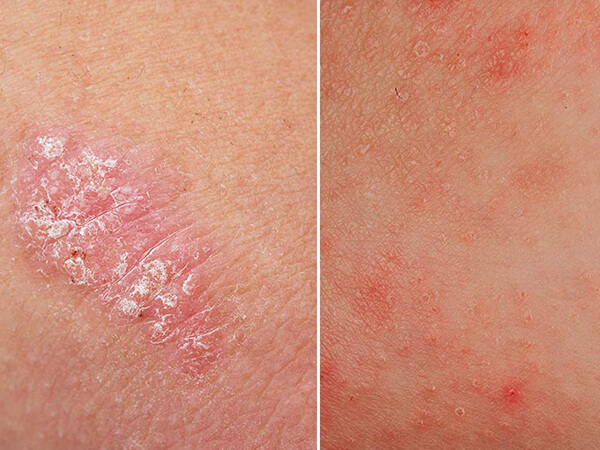
Eczema is a condition wherein patches of skin become inflamed, itchy, cracked, and rough. Some types can also cause blisters. Different types and stages of eczema affect 31.6 million people in the United States, which is over 10% of the population. Many people use the word eczema when referring to atopic dermatitis, which is the most common type. The term atopic refers to a collection of conditions that involve the immune system, including atopic dermatitis, asthma, and hay fever. The word dermatitis refers to inflammation of the skin.
Certain foods, such as nuts and dairy, can trigger symptoms. Environmental triggers include smoke, pollen, soaps, and fragrances. Eczema is not contagious. Some people outgrow the condition, whereas others will continue to have it throughout adulthood. This article will explain what eczema is and discuss its symptoms, treatments, causes, and types.
Contact Us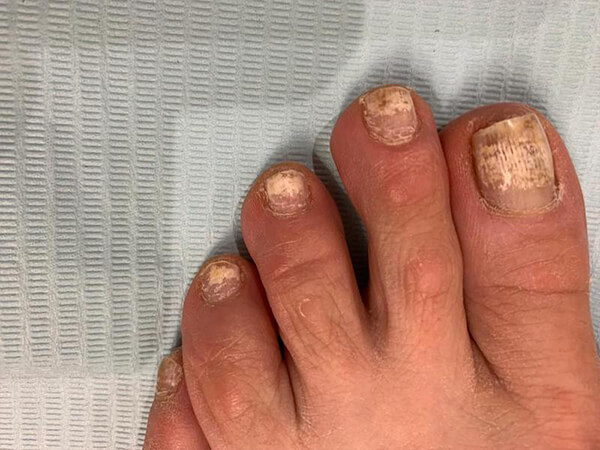
Healthy nails appear smooth and have consistent coloring. As you age, you may develop vertical ridges, or your nails may be a bit more brittle. This is harmless. Spots due to injury should grow out with the nail. Abnormalities — such as spots, discoloration, and nail separation — can result from injuries to the fingers and hands, viral warts (periungual warts), infections (onychomycosis), and some medications, such as those used for chemotherapy. Certain medical conditions can also change the appearance of your fingernails. However, these changes can be difficult to interpret. Your fingernails’ appearance alone isn’t enough to diagnose a specific illness. A doctor will use this information, along with your other symptoms and a physical exam, to make a diagnosis. You should always consult your doctor if you have any questions about changes in your nails.
Contact Us